

This example of sharing electrons between atom- B and the hydrogen atom is known as a hydrogen bond.
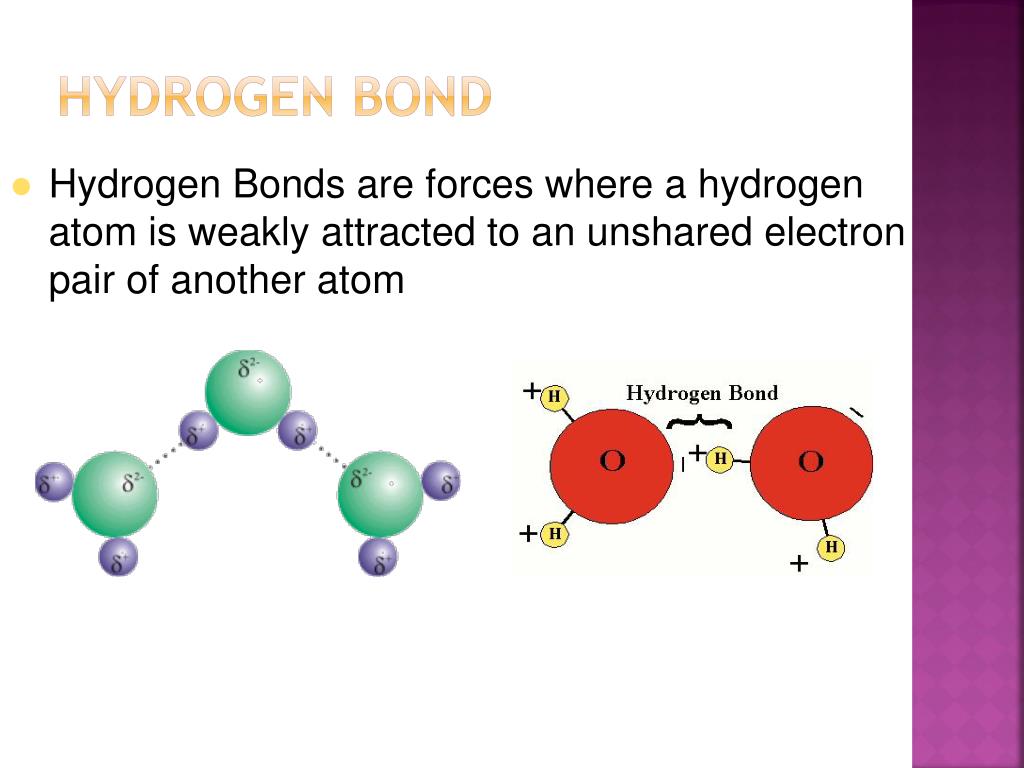
The atom -B would now want to share its electrons with the hydrogen atom. Now, we take an example of an atom -B, which has a lone pair and is in the hydrogen atom’s proximity. Since the atoms have opposite polar attractions, they are attracted to each other, i.e., and the hydrogen atom is attracted to the atom -A. We also have a Hydrogen atom in the example, which is electropositive in all cases. Here we have taken the example of an atom -A, which is electronegative. Hydrogen bonding can be explained through the following example: Ionic and covalent bond energy: 200 KJ/mole The atomic energy between these types of bonds are as follows: Hydrogen bonds are usually weaker than ionic and covalent bonds, but it is also important to note that hydrogen bonds are stronger than Van der Waal Force. And in certain organic chemical cases, the hydrogen atom also forms a chemical bond with carbon and chlorine (this falls under the umbrella of organic chemistry).įor example- hydrogen bonding is intermolecular forces between polar molecules of water, hydrogen bonding exists in ammonia molecules, and hydrogen bonding exists in hydrogen fluoride molecules. The chemical elements which usually form a bond with the hydrogen atom are fluorine, nitrogen, and oxygen. Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole force between highly polarized molecules. Hydrogen bonding is explained as the intermolecular forces between polar molecules. The electromagnetic forces between one section of the molecules are felt by the electrically charged molecules of the other section of the bonding. Hydrogen bonding occurs due to the attraction of two or more electrically charged molecules, which have a small electric charge known as a dipole, which translates to “two poles”.Īs you will see in the further sections of this article, one of the molecular poles is negative, whereas the other is positive. Hydrogen bonding occurs when the molecules of an element that contains atoms exert a greater pull on the covalent bond formed by the hydrogen atom resulting in the shared electrons orbiting the hydrogen atom more than the atom they are bonded to (referring to the covalent bond here).Ī hydrogen bond is a weaker form of the bond than the covalent bond formed by the hydrogen atom and another element.Ī hydrogen bond is comparatively stronger than a simple dipole-to-dipole bond but weaker than an ionic bond. The elements which form a bond with hydrogen have the following electronegative charge:Ĭhlorine -3 (the study of the formation of a hydrogen bond between the hydrogen atom and the atom of chlorine is known as organic chemistry) And finally, the atom must have a lone pair to share with the hydrogen atom, which must be smaller in size.

Also, the atom’s electronegativity must be equal to or greater than 3.
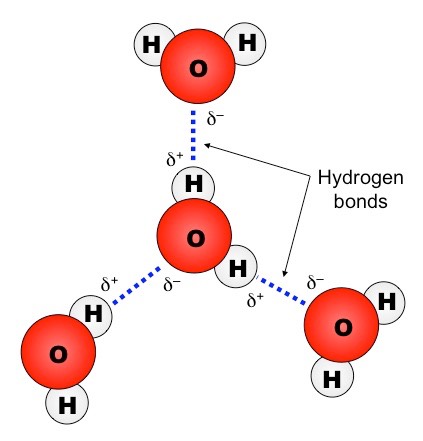
There are certain prerequisites for forming a hydrogen bond, such as the element forming a bond with the hydrogen atom must be electronegative. In the context of organic chemistry, it forms a bond with the elements of carbon and chlorine. The hydrogen atom forms a bond with mainly the chemical elements of fluorine, nitrogen, and oxygen. The nature of a hydrogen bond is either dipole-dipole type, ion-dipole type, or dipole-induced dipole type. Hydrogen bond definitionĪ hydrogen bond can be explained as a weak bond created between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative element that has a lone pair to share with the hydrogen atom to create an electrostatic attraction between portions of the molecule of the two atoms. A covalent atomic bond is also referred to as bonding pairs or shared pairs. A hydrogen bond, also expressed as an H-bond, can be defined as the electrostatic bond of a hydrogen atom with a covalent bond of another electronegative group of elements or atoms.Įlectrostatic force can be explained as the force generated between two objects (in the case of a hydrogen bond- between two atomic particles) due to electric charges, which makes the two bodies attracted towards each other.Ī covalent bond can be explained as a chemical bond between two atomic particles, which is created due to sharing of electron pairs between the two respective atomic particles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
